For most flash systems the above solvent switching is a manual operation. With such stationary phases retention time is longer for molecules which are less polar while polar molecules elute more readily.

Diagram Of Normal Phase Chromatography Separation The Stationary Phase Download Scientific Diagram
Uses substances with high polarity in the stationary phase.

Hplc reverse phase to normal phase. The only other issue is the changeover to normal phase. Flush with tetrahydrofuran 4. However if you intend to use normal phase 100 of the time then you should switch the pump seals and the seal in the metering device.
Normal phase was one of the first developed separation methods and for this reason reversed phase LC was labeled just that as it involves stationary and mobile phases with the reversed polarities. Reversed phase columns are one of the most popular modes in HPLC analysis. One common stationary phase is a silica which has been surface-modified with RMe 2 SiCl where R is a straight chain alkyl group such as C 18 H 37 or C 8 H 17.
It is great when a compound is too hydrophobic or hydrophilic for reverse-phase HPLC. Ecient Conversion of HPLC Instruments between Normal-Phase and Reversed-Phase Solvents Richard Henry and Carmen T. Today a polar functional group is bonded to silica which is advantageous when analytes.
Flush with methylene chloride 5. Thermo Scientific reversed phase LC columns are available in an array of chemistries to optimize separations and provide enhanced retention or changes in elution order. The separation is based on the analytes ability to engage in polar interactions eg hydrogen bonding or dipoledipole type interactions with the sorbent surface.
Depending on which column is used for HPLC the substances that can be separated are different. HPLCReverse PhaseNormal Phase. If you plan to switch back and forth stick with the reverse phase standard seals.
Flush with chloroform 4. To switch from reversed- to normal-phase prime with methanol or acetonitrile followed by ethyl acetate and then hexane all between 50 to 100 mL. Flush with methanol 3.
Flush with HPLC grade water. It can also be used for isomer separation if the sample injection solvent is non-polar or if recovery in non-polar solvents is desirable. Uses highly hydrophobic materials in the stationary phase.
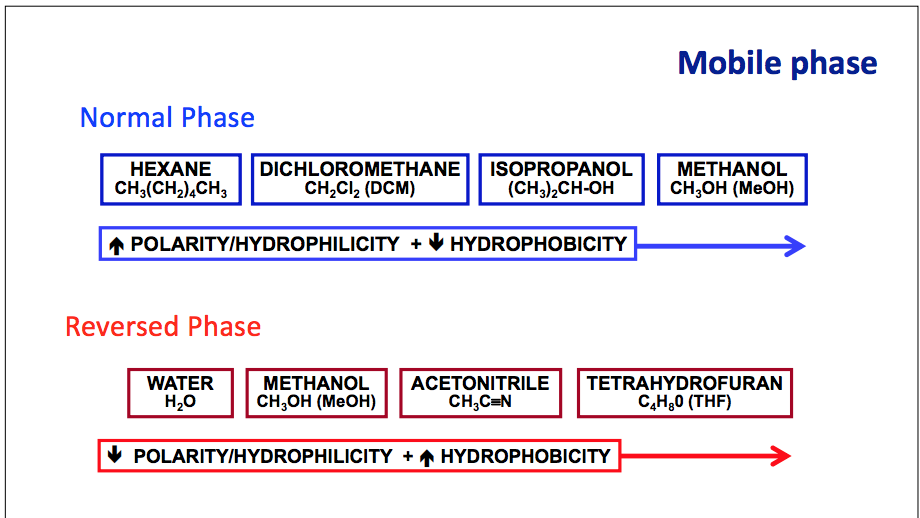
The key difference between reverse phase and normal phase HPLC is that the reverse phase HPLC uses a nonpolar stationary phase and a polar mobile phase whereas the normal phase HPLC uses a polar stationary phase and a less polar mobile phase. Although this type of chromatography isnt used as often there are many good reasons to choose Normal Phase HPLC. Flush with methanol 3.
Figure S-2 illustrates the black three-dye mixture being separated using such a protocol. Check with Agilent to be sure. Whereas in normal HPLC the non-polar parts of a substance are separated at the stationary phase thus eluting the polar ones afterwards in reverse HPLC the polar ones are subtracted first.
Reversed phase HPLC RP-HPLC has a non-polar stationary phase and an aqueous moderately polar mobile phase. The term reversed-phase describes the chromatography mode that is just the opposite of normal phase namely the use of a polar mobile phase and a non-polar hydrophobic stationary phase. It has an increased reproducibility of the retention time when compared to normal phase chromatography.
If you have the older. Flush with benzene-free n-hexane VII-2. Normal phase LC involves a combination of a polar stationary phase and a less polar or even nonpolar mobile phase 4.
Inject 4 aliquots of 200 µL DMSO during this flush 2. Normal-phase HPLC NP-HPLC which is not the most popular form of HPLC nowadays utilizes a polar stationary phase usually silica and less polar nonaqueous eluting solvents eg n-hexane and ethyl acetate mobile phase. Normal phase media 1.
The rotor seal in the autosampler may also require replacement. Reversed phase media 1. With the new Selekt system this process is now automated which is really convenient.
Flush with tetrahydrofuran 2. In general however high-performance liquid chromatography uses reversed-phase chromatography. Reverse-phase chromatography is a type of recent HPLC.
After finishing the working with reverse phase mode wash the entire systemA-LineB-LineC-Line D-LineNeedle wash and Seal wash etc with water to remove residue of BufferDo not keep any reverse phase solvent on HPLC systemAlways use isopropyl alcohol as reservoir during the working with normal phaseAfter washing the HPLC System. This is achieved by using lipophilic groups in the stationary phase as. Basically this increase of the reproducibility is achieved by making the stationary phase non-polar.
This video contains complete explanation of Reversed phase chromatography and Normal phase chromatograpgy Video is very useful for students of chemistry background such as biochemistrypharma. Difference Between Reverse Phase and Normal Phase HPLC.

High Performance Liquid Chromatography Wikipedia

Hplc Normal Phase Vs Reverse Phase Hplc Animated Youtube

Chemistry Net Normal Phase Liquid Chromatography Lc Hplc

Difference Between Reverse Phase And Normal Phase Hplc Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Solved Im Confused By This Diagram For Reverse Phase Hpl Chegg Com

Difference Between Reverse Phase And Normal Phase Hplc Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Stationary Phases And Mobile Phases Used In Normal Phase And Reverse Phase Download Scientific Diagram

Hplc Normal Phase Vs Reverse Phase Video Technology Networks

Hplc Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography Animation Rplc Youtube




